Is long-term memory used in a visuo-spatial change-detection paradigm?
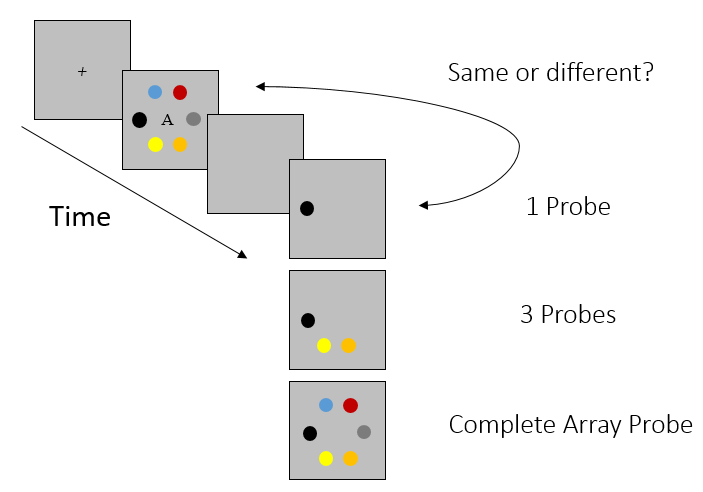 Image credit: [BG]
Image credit: [BG]
Abstract
In tests of working memory with verbal or spatial materials repeating the same memory sets across trials leads to improved memory performance. This well-established “Hebb repetition effect” could not be shown for visual materials in previous research. The absence of the Hebb effect can be explained in two ways. Either persons fail to acquire a long-term memory representation of the repeated memory sets, or they acquire such long-term memory representations, but fail to use them during the working memory task. In two experiments, (N1 = 18 and N2 = 30), we aimed to decide between these two possibilities by manipulating the long-term memory knowledge of some of the memory sets used in a change-detection task. Before the change-detection test, participants learned three arrays of colors to criterion. The subsequent change-detection test contained both previously learned and new color arrays. Change detection performance was better on previously learned compared to new arrays, showing that long-term memory is used in change detection.
Links to all co-authors: